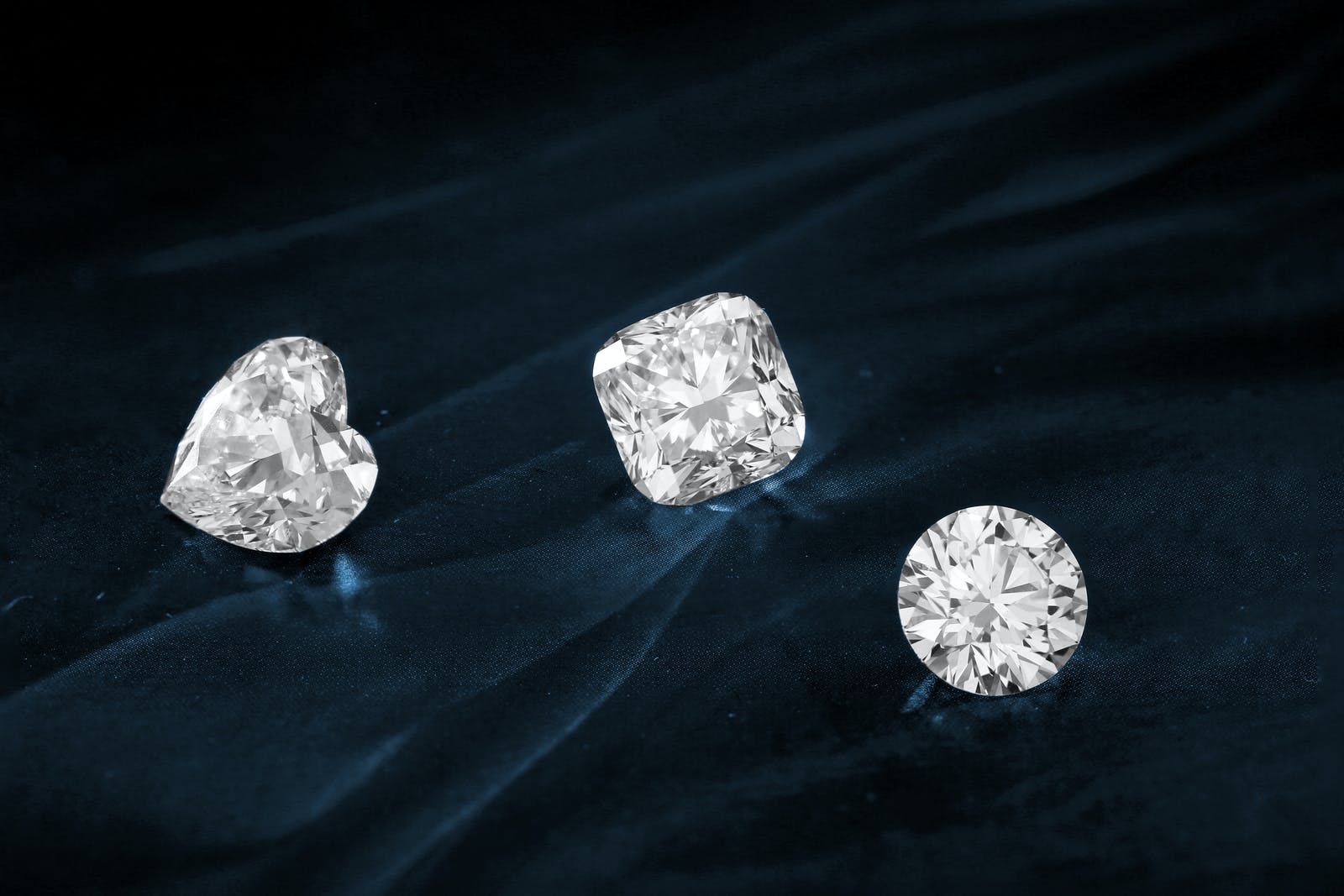
CVD Diamonds are created in laboratories, but they’re perfectly beautiful and indistinguishable from mined diamonds to the naked eye. So, what makes CVD Diamonds valuable? As CVD Diamonds are comparable in colour, clarity, and cut to mined diamonds, they can be sold at a fraction of the price, making them an amazing value for the consumer that doesn’t compromise on beauty or quality. Here’s why CVD Diamonds are still one of the most valued diamond types available in today’s market, even after the introduction of Lab Grown Diamonds (LCD).
CVD Diamonds Are Real Diamonds
CVD diamonds are not synthetic, they’re real diamonds. The difference is that the diamond is grown through a process called Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This process starts with a tiny diamond seed which can be as small as 10 microns. A high-purity crystal is placed on the seed and covered with chemicals that produce carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas lab created diamonds. Inside an oven, the gases react to create a thin layer of diamond crystal on top of the seed.
It takes anywhere from one week to four months to grow a single stone this way, but many stones can be grown at one time due to advances in technology and laser techniques for cutting them.
CVD Diamonds Are Grown In A Laboratory
CVD (chemical vapour deposition) diamonds are grown in a laboratory by placing carbon and hydrogen gas onto a diamond seed, or small piece of diamond. The gas dissolves into the molten diamond to form tiny polycrystalline ‘diamond grains’. These grains are then used to grow a large synthetic diamond crystal. The process involves exposing the growing diamond to high-energy particles that remove nitrogen atoms from the surface. This leaves behind a pure carbon surface with an extremely low defect rate. The diamond is grown at atmospheric pressure but very high temperatures inside a vacuum chamber. What is the value of CVD Diamonds in today’s market?
What makes this process so valuable is how it has been applied to create superior gemstones in natural settings such as pearls, sapphires, rubies and emeralds. Once they are cut and polished they will look indistinguishable from natural gems as their flaws cannot be seen under a microscope.
The Price Of CVD Diamonds Is Lower Than Mined Diamonds
CVD diamonds are created through a process known as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This process is different from the way that mined diamonds are made, which is why they are priced differently. For example, mined diamonds were once considered to be more valuable because they were believed to be rarer than man-made stones. However, discoveries have shown that there are more CVD gemstones than those found in nature. Additionally, many people believe that man-made gems are worth less because they lack the intrinsic value of a natural stone. However, this does not take into account other factors such as durability and rarity when considering the price.
CVD Diamonds Are Available In A Wide Range Of Colours
CVD diamond is a process that has been introduced to the market to create diamonds with colourless clarity. This is achieved by putting a thin layer of atoms on top of the diamond during the growth process. There are many advantages to this, for example, there are seven colours available: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. This means that you can have any kind of colour you like on your diamond and it will still be considered white. Many people think that lab grown diamond growers are not worth much because they are less expensive than natural diamonds. But it doesn’t matter what type of price tag the diamond has; if someone likes the design and the colour then it has value to them.
CVD Diamonds Are Used In Jewellery And Industry
CVD diamonds are created through a process that chemically mimics the natural process of crystallization, without all the time and expense. This means that for those looking for affordable, quality jewellery, CVD diamonds may be a perfect choice.
CVD diamond stones are available in round brilliant cuts that range from 0.25 carats to 5 carats, as well as princess cuts and marquise cuts. Their size allows them to be easily integrated into any type of jewellery design. The colour ranges from white to near-colourless, with most falling somewhere between G-H on the colour scale.